Warehouse Automation To Make Your Business At The Ready For The Future
Updated on December 30, 2021
Increased customer demand and booming e-Commerce make business owners introduce warehouse automation. It helps to strengthen labor management and gain more customers satisfaction.
Data-driven and automated warehouse processes contribute to an overall supply chain efficiency nowadays due to the cost reduction for the company and meeting the needs of the customers.
In accordance with G2.com, business software, and services reviews platform, 2022 will start with 620 000 robots and AGV’s shipped worldwide in comparison with only 40 000 in 2016, and with more than 40% of companies ready to invest in shuttle systems for warehouse automation. “One-day deliver” standard launched by Amazon is no longer an outstanding performance, but a “must-have”.

Jeff Sierra, a Senior Coaching Advisor in “Mind Fuel”, said in the “Eight Experts Thoughts About Warehouse Automation”: “The misconception about technology’s role is presented nowadays in many businesses. They think warehouse automation is to do all the processes and all the thinking. One needs to understand the nature of automation and develop well-defined surrounding processes to maximize ROI”.
What Is Warehouse Automation
Businesses treat warehouse automation as the optimization of the goods flow into, within, and out of the premises to the clients with the least human assistance possible. Illustrating the core sense of automation, DHL emphasizes that replacing repetitive manual tasks with robots boosts the improvements in “one of the biggest warehouse tasks”, which is “picking”.
Picking is not only one action of moving an item around the vast warehouse premise. There are some processes associated with it: finding a specific item, random bin picking, co-packaging, sorting orders, placing objects onto conveyor belts. Warehouse automation can be responsible for all these duties performing robotics process automation, inventory software management, and even property mapping or space cleaning.
Thus, for example, Amazon’s smart automated warehouse is able to process 50% more stock due to the robots (30 cm high) being able to move 450 kg in weight. This way of automation applying effective robots performs 3 times faster operations than they can be completed by humans.

Warehouse automation focuses both on digital processes (inventory management, returns processing) improvements as well as the physical ones (picking, packing). But it doesn’t mean it steals humans’ jobs, it just augments man’s abilities, replacing tedious manual tasks freeing time for more complex duties.
Types of Warehouse Automation
According to the President of Westfalia Technologies, Dan Labell, “the warehouse is the last spot to reduce any kind of the logistics costs and expenditures of the long-term distribution”. And we can reach this reduction by applying a variety of warehouse automation types:
- If business owners are striving to optimize the goods or spare parts movement around the warehouse premises, Goods-to-Person (GTP) technologies bring the materials to workers for assembling. GTP technologies comprise automated storage and retrieval solutions utilizing vehicles to move the items throughout the warehouse;
- Once there’s the necessity to manage workers’ labor in cases of items search, Pick-to-Light and Put-to-Light Systems come in handy. They use barcodes and LED lights to augment human activities assisting in items’ locating. The difference between Pick-to-Light and Put-to-Light solutions is the direction of goods flow: while Pick-to-Light technology assists in finding inventory positions, Put-to-Light is a reverse activity of arranging the incoming positions grouped in accordance with any criteria (e.g.positions necessary for one box of the customer’s order);
- Voice Picking and Tasking ensures the efficiency of cross-communication workers’ activities throughout the warehouse utilizing wireless headsets. Voice picking and tasking can target sorting things as well;
- To unify the process of sorting, sometimes managers invest in Automated Sortation Systems. They help to identify, sort and direct the items to the specific locations being based on sensor and barcode technology. This group of solutions is quite an independent one from human interventions;
- AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robots) and AGV (Automatic Guided Vehicles) are also free of human interventions. Both types of warehouse automation have the objective to minimize human manual activities.

Intel insists AMRs are the revolutionary solution bringing the most benefits for the whole supply chain. They explain that both AMRs and AGVs enhance labor safety, hence, reduce administrative costs.
Robots increase flexibility because they do not need the direct operator’s supervision and are able to address the surroundings performing a variety of tasks. Warehouse automation solutions let workers concentrate on high-value activities, freeing time and energy.
Analyzing every possible way to automate the warehouse, Forbes divides all the robotics solutions mentioned above into robots similar to “man style” and “collaborative robots” working in collaboration with other workers. Robots totally replacing manual labor give an opportunity to change working conditions and cut costs dramatically (e.g. robots do not need air conditioning or a certain level of light).
Automated inventory and warehouses tackle a lot of challenges we mentioned, but the critical thing your ROI will depend on is the right time to launch automation and the right steps to implement it. Let’s shed some light on these two points further.
When To Automate Your Warehouse
Warehouse automation demands investments. So, to allocate financial resources wisely it’s reasonable to follow a checklist. They will help to address the most crucial issues. Let’s start with your administrative costs estimation: too many workers and still warehouse operations are time-consuming or you estimate KPIs and find out business experiences delays and returns.
These are the first signs something goes wrong and it’s high time to analyze which of these options can be optimized:
- Your current warehouse operations are too time-consuming and labor-intensive;
- Order fulfillment is not accurate;
- Shipping in time is always a challenge;
- Inventory count errors occur often;
- Inconsistencies appear in shipping, receiving, picking, and stocking;
- You’ve got many returns and hardly gained a high level of customer satisfaction.
It can be complicated to identify the bottlenecks on your own, and further decide on which custom solutions you need to apply, that is why we remind you Innovecs provides detailed consultancy in the field of warehouse automation. During the consultation and your business needs research we can develop a step-by-step plan of the warehouse automation or identify the fields striving for automation first of all.
How To Automate Your Warehouse
Full warehouse automation may have both pros and cons. Of course, you’ll gain more control over the slightest processes, but it’s still time-consuming to build up a custom warehouse automation solution. Custom solutions bring a lot of flexibility, but at the same time, you’ll need a lot of expertise and specialists ready to adjust, maintain, and develop automated warehouse systems.
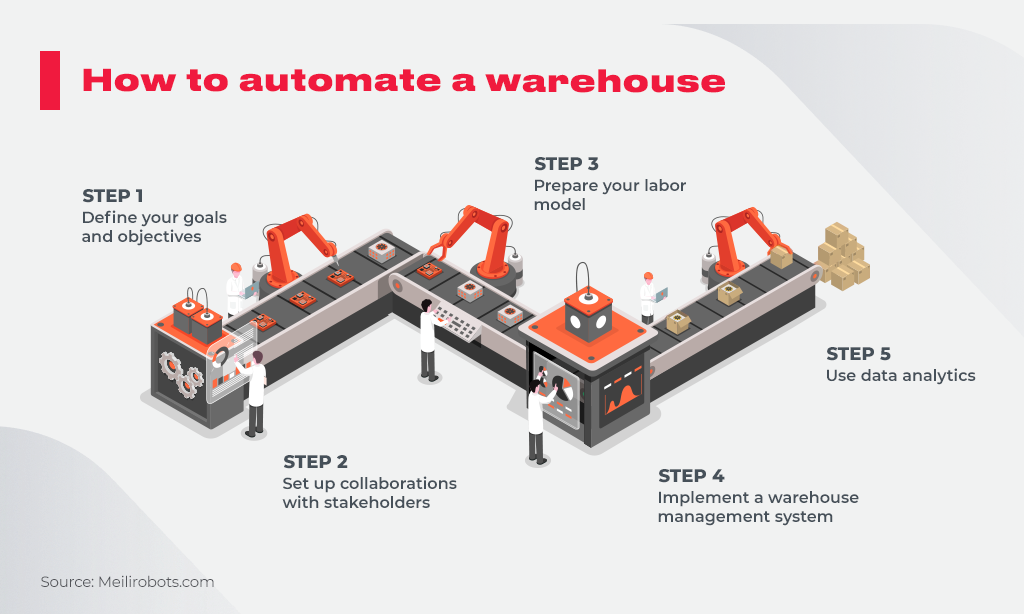
It doesn’t matter whether you choose custom solutions or ready to use out-of-the-box ones there are some steps you need to follow:
- defining of the goals and objectives (ask precise questions to yourself, brainstorm with the key managers to identify how picking accuracy increased from 92% to 99% will contribute totally to your customers’ satisfaction and company revenue);
- looking for the bottlenecks you are willing to tackle define what exact errors you want to remove, and how this result in ROI and profit;
- set up the cross-department communication involving all the stakeholders to understand better how automated systems should work to bring higher performance;
- prepare your own labor model using key metrics essential for your business (e.g. injures rates you want to decrease or daily picking volume of the goods you wish to perform without men’s labor);
- development of new WMS and its integration with the existing one (it’s obvious you’ll not replace the whole system at once, so integration becomes part and parcel of the automation process);
- analyze your data on a regular basis to iterate the developed software and make it more sensitive to the critical benchmark of your business productivity.
Key Challenges in Warehouse Operations and Common Ways to Overcome Them
In general, warehouse management is a complicated, multi-layer process consisting of multiple operations, including inventory management, quality control, sales, and distribution, among others.
It is difficult to maintain all these operations and make them flow smoothly to avoid unforeseen issues, such as mistakes in order fulfillment or shipment delays.

Overall, businesses face many challenges in warehouse operations, specifically inventory count inaccuracies, lack of picking optimization, and poor performance visibility. Let’s find ways to overcome these challenges through warehouse automation tools.
Inventory Count and Control Difficulties
Many e-commerce businesses face difficulties with maintaining an accurate inventory count in their warehouses or distribution centers. The process of counting all products may take days or even weeks depending on the warehouse size and the volume of stored products.
If counting is performed physically, it is impossible to avoid inaccuracies. Human errors occur all the time. To minimize the number of these errors, businesses often turn to cycle counting, which means they break counts into smaller and more manageable iterations to reduce the number of errors but not get rid of them at all.

Solution
To overcome the challenge of maintaining an accurate inventory count, retailers can implement warehouse automation through a variety of solutions. The two widely used inventory management tools are barcode labeling and radio-frequency identification (RFID).
Barcode labeling
Barcode labeling is the core of the entire process. All products are marked with a label containing their information, which can be gathered by scanning the barcode.
Information about all labeled products is stored in a warehouse inventory system (WIS). Thus, it becomes difficult to lose goods during, let’s say, order fulfillment because all of them are tracked through the WIS.

Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID)
The RFID technology is similar to barcode labeling, but it provides more benefits:
- While barcode labels are printed on paper and can be used only once, RFID applies reusable tags that are humidity and temperature proof.
- RFID allows you to scan multiple items at the same time from up to 50 feet away, significantly saving you time.
- RFID chips can store more data than barcodes and can also be encrypted.
However, the implementation of RFID technology is more expensive than barcodes, which, in fact, provide similar sets of capabilities.
A solution based on either barcodes or RFID tags can prevent loading the wrong pallets onto trucks by installing sensor controllers at gates. All orders that cross the gate line are scanned and validated. If the one includes the wrong items, the controllers track this and notify the system.
Lack of Picking Optimization
When it comes to picking, a lot of problems may arise.
First, it may take lots of time for a picker to find the right goods in the warehouse to collect the order.
Second, sometimes pickers select the wrong products or quantities and forward them for packing. As a result, customers are dissatisfied because they receive goods they did not ask for.
Third, with the lack of picking prioritization, urgent orders may be neglected while less important ones are being fulfilled first.
Finally, picking routes across the warehouse are not optimized, which causes workers to spend hours searching for necessary goods.
All these problems may lead to labor-intensive picking full of human errors.
Solution
To overcome order picking challenges, retailers have implemented warehouse management systems (WMS) into their operations. These systems have many features that can help optimize picking routes and eliminate the problems described above.
Such systems store information about all goods, including their coordinates in the warehouse and expiration dates. When the picklist for an order is formed through this system, it generates optimized routes based on the coordinates and expiration dates. It means that the picker will spend less time walking between pallets and will collect the goods that will expire first.

A WMS can allow you to create picking routes based on different approaches, with batch and wave being the most effective types.
Batch picking means that a worker takes the picklists of several orders and requests the system to build the route that will help pick products that coincide with these orders. It helps avoid repeated walks to the same locations to fulfill similar orders.

Wave picking involves breaking the order picklist into several parts based on the warehouse zones where necessary goods are located. This way, several pickers collect different products for the same order. Such an approach is perfect for orders that include products located at opposite ends of the warehouse.

Watch the video below to learn how Innovecs’ teams can automate the entire order management process, from receiving the order to picking and loading it on the truck.
Poor Performance Visibility
In the warehouse business, labor costs are huge. However, if human resources are used properly, these warehouse costs can be reduced without affecting overall performance.
Monitoring performance is complicated, especially when you have multiple departments. Performance visibility suffers, and it becomes difficult to assess the work of the department as well as the individual warehouse workers.
Without the right tools, you can’t understand what the general workload is and who is responsible for separate operations. Uneven workload distribution leads to lower performance and the inability to achieve key e-commerce business objectives.
Solution
To improve performance visibility, a labor-management system (LMS) can be integrated into your WMS. An LMS is a system aimed at controlling human resources operations within a warehouse.
While there are multiple ready-made solutions, software development companies, like Innovecs, can build a custom LMS with a required set of features that will suit your business.
Types of LMS
There are two main types of LMS: reactive and predictive.
- A reactive LMS stores information about already completed tasks and helps generate reports so the management can see the volume of work that has been done for a certain period of time. This is a “post-fact” system that only stores information and creates reports without the possibility to set KPIs and describe steps for achieving them.
- A predictive LMS includes features for estimating the time needed for completing a certain task. Such systems often have a more complicated architecture as compared to reactive ones, and they require more input data from the worker.
For example, to estimate the time needed to fulfill order X, the system requests a worker to provide a picklist with goods quantity and coordinates. Based on the routes built by WMS, a predictive LMS calculates the approximate time needed to fulfill the order.

For one logistics company, Innovecs’ team of engineers developed a custom labor management system as a part of a WMS that allowed for tracking all tasks, controlling time, and generating comprehensive reports. Our system helped significantly increase employee productivity.
Top Global Cases of Successful Warehouse Robotic Process Automation
It is estimated that the warehouse automation market will grow by more than twice in 2025, approaching $27 billion (at CAGR of 11.7%). This can be explained by the fact that global e-commerce and retail businesses, such as Amazon, Walmart, and Alibaba, invest more and more in warehouse automation.
Let’s see how these e-commerce giants automated their warehouses to reduce labor costs and eliminate human errors.
Amazon Warehouse Automation
At the beginning of 2019, the biggest e-commerce company in the world, Amazon, started testing warehouse automation technologies that can make order packaging processes 5 times faster.
The workflow is as follows: workers put goods on the conveying belt and robots scan them and pack them into boxes. This way the machine can process 700 orders per hour.
Reuters states that Amazon now uses such an approach in several warehouses, but they plan to implement this sort of automation in the majority of their locations. According to their calculations, each machine can do the job of 24 people.
Amazon applies the Italian CartonWrap robots and their own SmartPac machines. Although all of them still require human control, they help boost performance and reduce labor costs.
Walmart Warehouse Automation
Walmart is another great example of warehouse automation. In 2016, the company started testing drones to keep track of their warehouse inventories. This way, they could easily find lost goods. While a human could spend a month searching for a product in a warehouse, the drone managed to do it within a day.
Also, Walmart has found a way to automate their order fulfillment process by using the Alphabot robot in its distribution centers. This machine was created by Walmart in partnership with Alert Innovation.
The robot works by first gaining access to Walmart’s inventory system. It’s then permitted to retrieve information about the orders made online. Second, Alphabot reads this information, checks the warehouse layout, finds necessary goods, and delivers them to workers for packaging. Just like Amazon’s robots, these ones also require partial human intervention.
Alibaba Warehouse Automation
It is said that Alibaba is a Chinese Amazon, which is true in part because this e-commerce giant is also turning its warehouse into a smart robotic environment.
In China, the job market is huge, but the cost of labor is constantly growing. This is one of the reasons why many companies have implemented autonomous technologies based on artificial intelligence. In 2017, the number of robots in China exceeded 100,000, which is more than in the USA and Europe combined.
Alibaba is using robots for segregating supplies in one of the warehouses in Huzhou. They are controlled via Wi-Fi, are taught to make 360 degrees turns, and bypass obstacles due to special in-built sensors. Moreover, when their battery runs out, they move to the charging stations without any instructions.
Summarizing the Value of Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation is a powerful method used to overcome the majority of the challenges you face in warehouse operations.
- First, by implementing an inventory management system into your operations, you improve inventory control, get rid of count inaccuracies, and minimize the number of human errors.
- Second, by implementing a warehouse management system, you reduce costs associated with order fulfillment mistakes and eliminate shipment delays.
- Third, by integrating a labor-management system, you enhance employee productivity and cut labor costs.
If you need to develop a system to automate your warehouse operations, do not hesitate to send us the requirements, and we will think over the best services we can offer.