What is the Impact of Big Data in Logistics and Supply Chain
Disruption and uncertainty. This is how PwC described ever-changing customer behavior. Today, B2B companies demand quicker shipments with more cost efficiency and visibility, while B2C customers show persistence in going digital. What is the outcome? Retailers and supply chain players are jumping on the tech bandwagon to keep afloat.
E-commerce giants like Amazon and Alibaba have already done it. They relentlessly focus on big data to expand market growth and build logistics networks to reach even remote rural areas. Following the official news, Alibaba is going to handle 1 billion parcels per day and do 24-hour delivery across China and 72-hour delivery internationally. The reason behind this rapid expansion is correct big data usage.
Big data in logistics are considered the major driving force. It is an absolute must for developing a strong, competitive advantage. As the Annual Third-Party Logistics Study says, about 98% of 3PLs admitted their further progress largely depends on data-backed decisions. More than 80% agreed big data is “a core competency of their supply chain organizations.”
Why make so much fuss about it? The answer is quite straightforward: Big data in logistics help enterprises reduce costs by 49.2% and drive innovation by 44.3% as Big Data Execute Survey 2017 claims.
The main challenge with big data, though, is to handle them right. Obviously, this can be achieved through logistics management software. The following 4 sections are a guide through the key choice criteria for software and possible big data uses.
Smart Logistics Tracking: Picking the Right Software
Why is this a big issue to solve? Big data in logistics come from too many sources: fleet GPS trackers, driving patterns, advertising response stats, and more.
Having big volumes of it causes chaos and impedes business success, whereas structured data favors predictive analytics. Therefore, picking up the right logistics management software matters a lot.
A truly powerful solution handles everything from supply chain mapping to inventory tracking, to warehousing improvement (picking, packing, shipping, etc.), to route optimization, etc. The basic choice criteria of the software should include:
- multi-client architecture with a proper deployment model in place
- efficient costing and invoicing capability to issue invoices on time, apply and process partnership policies, etc.
- real-time logistics tracking to establish transparency, exchange shipping data, and improve accuracy
- all-inclusive reporting system with shipment records and history, etc.
Smart logistics and supply chain management require either one suite embracing all the functions, or a suite seamlessly integrating with other stand-alone solutions and big data analytics tools. The best way is to adopt a scalable and adjustable logistics management software, preferably cloud-based with a suitable chain management architecture.
Why is this a number one choice? A great many businesses partner with 3PLs, and they, in turn, cooperate with cargo or parcel carriers like DHL or FedEx. With so many partners on board, there must be a chance for them to draw analytics or data from any partner’s software and decide about goods transportation from a warehouse to the stock, course-correct routing, and so on.
Incorporating big data analytics tools pays off in big bucks. One of the largest parcel carriers, UPS, has finally rolled out its ORION algorithm (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation). It optimizes parcels movement throughout the network.
ORION now builds routes for more than 55,000 drivers in Northern America and cuts down the total amount of miles by 100 million per year.
Here comes one of the most successful big data use cases in logistics. It is route optimization.
Ongoing Route Optimization and Planning
Why is that important to logistics companies? It allows for saving budgets and avoids late shipments and deliveries. This is when you need to carefully make estimates. Putting too many drivers on one route results in higher costs, while putting too few of them leads to delays.
Smart transportation should embrace a few ever-changing factors:
- road repairs
- unfavorable weather conditions
- changing fuel prices
- fleet shortage, etc.
All these planning hurdles can be prevented with big data analytics. Big data in logistics favor dynamic planning of routes taking into account these changing factors, truck sensors, fleet repair schedules, real-time delivery status, and more.
UPS is a good illustration of how it works in the real world. The logistics giant has been collecting terabytes of useful data since the ‘90s which has helped UPS understand where they were and what direction they had to take next. Being picky with the data, they managed to save up to $50 million annually in the US by simply reducing one mile per driver.
With the ORION algorithm, UPS expects to achieve the maximum in the route optimization. Although the project itself costs $1 billion a year, the game is worth the candle. ORION is able to handle 250 million data points and produce thousands of optimized navigation opportunities every minute. Based on telematics and advanced algorithms, it carefully tracks driving patterns and signals when additional driving training is required. UPS has gone the extra mile to develop another smart transportation algorithm. It predicts when truck maintenance is required to avoid sudden breakdowns and late deliveries.
And what about warehousing? Let’s dig in.
Taking Warehouse Management to the Next Level
Optimization of warehouses management is another use case for big data in logistics. When combined with connected devices and automation, it brings more valuable insights into how the loading, carrying, and delivering should be done. For instance, by carefully planning the routes for forklifts and trucks carrying inbound and outbound freight, a company can enhance safety and save on petrol costs.
Traditional methods of managing warehouse operations like ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and legacy systems have lost their efficiency. What customers need is real-time updates on product availability, the manufacturing details, and possible delivery dates. In this case, big data analytics help trace changes in customer behavior and foresee their manufacturing preferences.
This contributes to smart logistics and supply chain management and enables companies to expand their operation, simplify distribution, prevent risks, achieve faster shipments, and most importantly, develop omnichannel strategies. Powered by AI algorithms, logistics companies are able to get more insights into products, freight shipment methods, shipment locations, and more. What should be done first to embrace the power of big data in warehousing? Here are some suggestions:
- Transmit data to the cloud
- Make data collection automatically
- Make use of the Internet of Things, GPS trackers, wearables, Wi-Fi, etc. to connect devices
- Evaluate the data quality
- Take cybersecurity precautions
- Define action algorithms based on the data collected
The Last Mile Risk Resistance: Tracking Management
The final challenge on our list is last-mile delivery. It has turned into a huge problem to solve as consumer impatience to obtain their orders asap keeps growing.
Another issue is a growing number of customers do not want to pay delivery fees urging e-commerce players and logistics providers to bear the cost. The stats shared by Business Insider proves these turn into a major expenditure.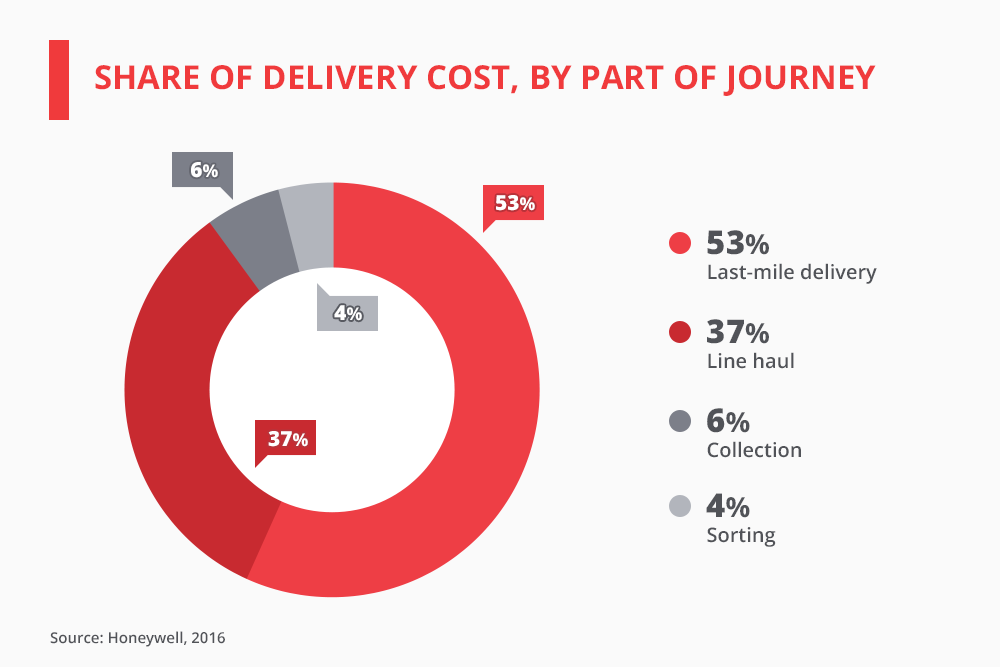
With route optimization based on big data, logistics companies have the chance to significantly improve last-mile deliveries. Real-time statistics on vehicle movement and data-driven operation let supply chain companies make same-day deliveries happen.
Big data backed up by the connected device’s network contributes more to last-mile delivery tracking from start to finish. This approach has been used by many big carriers like German-based DHL. The company has launched a new, efficient service, DHL Parcel Metro, enabling same and next day deliveries in Dallas and Washington D.C.
Plus, DHL has developed Smart Truck to enhance route planning based on the data taken from GPS trackers and roads. The telematics databases allow drivers to receive quick route updates and avoid traffic jams caused by accidents, weather conditions, etc. So far, Smart Truck has decreased the total number of miles by 15% helping reduce fuel consumption and lessen CO2 emissions.
Plus, DHL has developed Smart Truck to enhance route planning based on the data taken from GPS trackers and roads. The telematics databases allow drivers to receive quick route updates and avoid traffic jams caused by accidents, weather conditions, etc. So far, Smart Truck has decreased the total number of miles by 15% helping reduce fuel consumption and lessen CO2 emissions.
Some final words about big data in logistics
There is no doubt big data in logistics brings consolidation throughout the supply chain deliverables. The main point is to interpret the collected data in the right way. It is insufficient to get insight. One should be aware of the impact it can make and further steps to be taken.
Every data set should be wisdom, granularly measured. Where can this approach lead logistics in the future? Most likely to AI-powered algorithms suggesting a bunch of optimal solutions to choose from like AR-powered warehousing to improve slotting, thousands of robots for performing cargo picking, etc. Hopefully, these transformations soon become exploited to the best advantage.